
Subscriber Database: Core network also hosts the subscribers database (e.g.

These stats, alarms and traces form important tools for a network operator to monitor the network health and performance and improvise on the same. Network statistics collection (Performance Management), alarm monitoring (Fault Management) and logging of various network nodes actions (Event Management) also happens in the O&M centre. Number of subscribers, peak hour call rate, nature of services, geographical preferences are some of the factors which impact the configuration. O&M: Operations & Maintenance centre or Operations Support Systems to configure and provision the core network nodes.Physically, one or more of these logical functionalities may simultaneously exist in a given core network node.īesides above-mentioned functionalities, the following also formed part of a telecommunications core network:
Gateway functionality is dependent on the type of network it interfaces with.
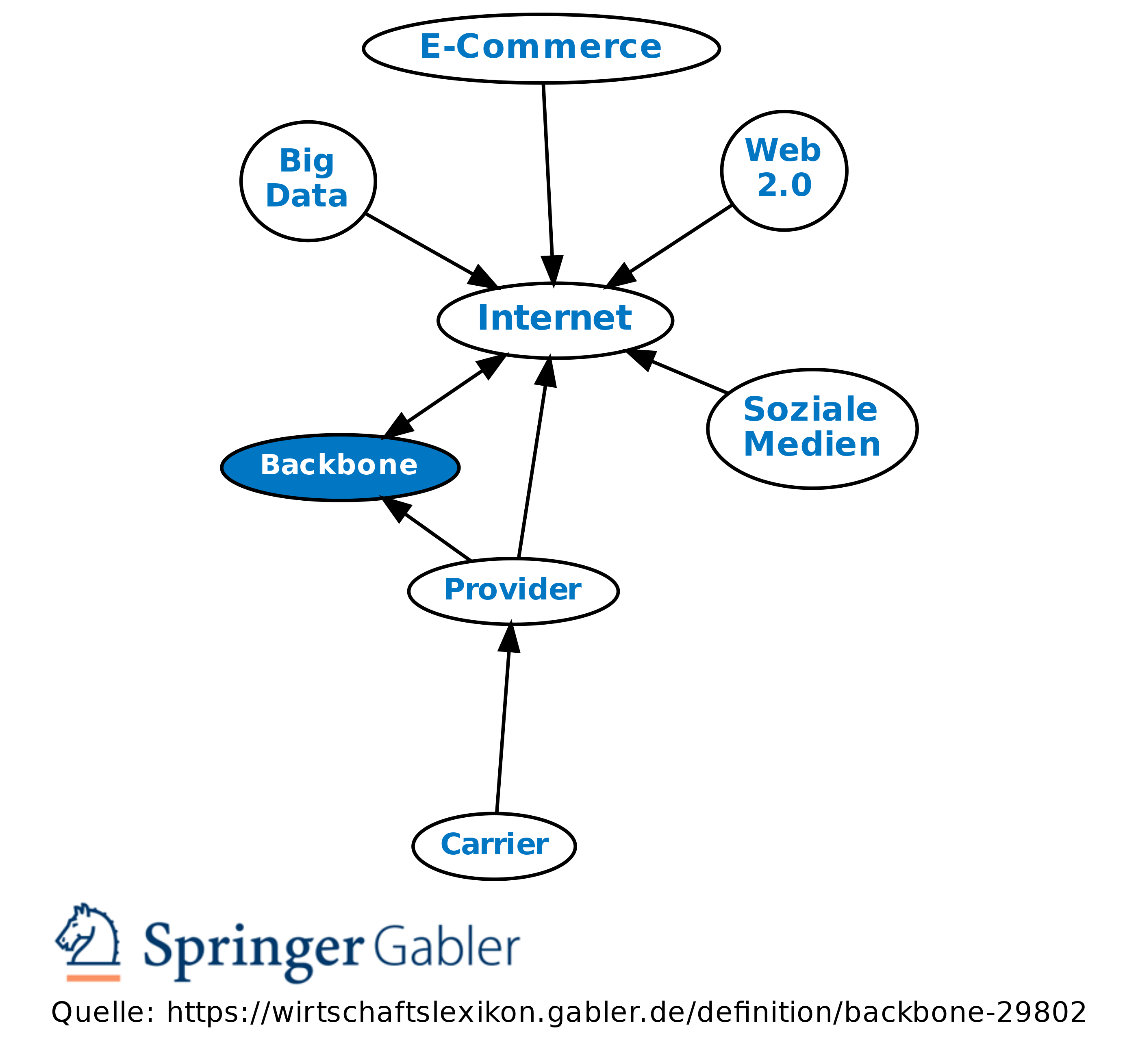

This makes backbone network essential to providing long-haul wireless solutions to provide internet service, especially to remote areas. Some large enterprises have their own core/backbone network, which are typically connected to the public networks.īackbone networks create links that allow long-distance transmission, usually 10 to 100 miles, and in certain cases - up to 150 miles. Many main service providers would have their own core/backbone networks that are interconnected. In the United States, local exchange core networks were linked by several competing interexchange networks in the rest of the world, the core network has been extended to national boundaries.Ĭore networks usually had a mesh topology that provided any-to-any connections among devices on the network. A core network provided paths for the exchange of information between different sub-networks. Typically the term referred to the high capacity communication facilities that connect primary nodes. One of the main functions was to route telephone calls across the PSTN. The core network was the central part of a telecommunications network that provided various services to customers who were connected by the access network. The theory, design principles, and first instantiation of the backbone network came from the telephone core network when traffic was purely voice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
